Molecular structures of yeast kinetochore subcomplexes and their roles in chromosome segregation
Abstract
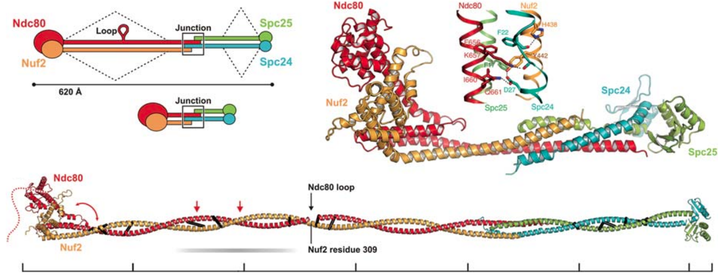
Kinetochore molecular architecture exemplifies “form follows function.” The simplifications that generated the one-chromosome:one-microtubule linkage in point-centromere yeast have enabled strategies for systematic structural analysis and high-resolution visualization of many kinetochore components, leading to specific proposals for molecular mechanisms. We describe here some structural features that allow a kinetochore to remain attached to the end of a depolymerizing microtubule (MT) and some characteristics of the connections between substructures that permit very sensitive regulation by differential kinase activities. We emphasize in particular the importance of flexible connections between rod-like structural members and the integration of these members into a compliant cage-like assembly anchored on the MT by a sliding molecular ring.