Recognition of divergent viral substrates by the SARS-CoV-2 main protease
Abstract
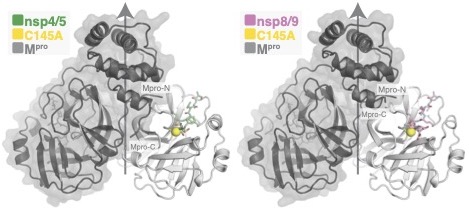
The main protease (Mpro) of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the cause of coronavirus disease (COVID-19), is an ideal target for pharmaceutical inhibition. It is required for infection, it cleaves the viral polyprotein at multiple sites, and it is conserved among coronaviruses and distinct from human proteases. We present crystal structures of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro bound to two viral substrate peptides. The structures show how Mpro recognizes substrates and how the peptide sequence can dictate catalytic efficiency by influencing the position of the scissile bond. One peptide, constituting the junction between viral non-structural proteins 8 and 9 (nsp8/9), has P1’ and P2’ residues that are unique among SARS-CoV-2 cleavage sites but conserved among nsp8/9 junctions in coronaviruses. Mpro cleaves nsp8/9 inefficiently, and amino acid substitutions at P1’ or P2’ can enhance catalysis. Visualization of Mpro with intact substrates provides new templates for antiviral drug design and suggests that the coronavirus lifecycle selects for finely tuned substrate-dependent catalytic parameters.