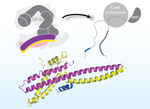
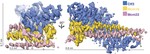
Recognition of centromere-specific histone Cse4 by the inner kinetochore Okp1-Ame1 complex
Successful mitosis depends on the timely establishment of correct chromosomal attachments to microtubules. The kinetochore, a modular multiprotein complex, mediates this connection by recognizing specialized chromatin containing a histone H3 variant called Cse4 in budding yeast and CENP-A in …
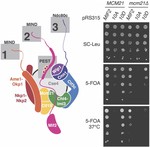
Multi-site phosphorylation of yeast Mif2/CENP-C promotes inner kinetochore assembly
Kinetochores control eukaryotic chromosome segregation by connecting chromosomal centromeres to spindle microtubules. Duplication of centromeric DNA necessitates kinetochore disassembly and subsequent reassembly on the nascent sisters. To search for a regulatory mechanism that controls the earliest …
The structural basis for Ulp2 recruitment to the kinetochore
The step-by-step process of chromosome segregation defines the stages of the cell cycle. In eukaryotes, signals controlling these steps converge upon the kinetochore, a multiprotein assembly that connects spindle microtubules to chromosomal centromeres. Kinetochores control and adapt to major …
Recognition of divergent viral substrates by the SARS-CoV-2 main protease
The main protease (Mpro) of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the cause of coronavirus disease (COVID-19), is an ideal target for pharmaceutical inhibition. It is required for infection, it cleaves the viral polyprotein at multiple sites, and it is conserved among …
The structural basis for kinetochore stabilization by Cnn1/CENP-T
Chromosome segregation depends on a regulated connection between spindle microtubules and centromeric DNA. The kinetochore, a massive modular protein assembly, mediates this connection and also serves as a signaling hub that integrates and responds to changing cues during the cell cycle. Kinetochore …
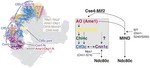
The structure of the yeast Ctf3 complex
Kinetochores are the chromosomal attachment points for spindle microtubules. They are also signaling hubs that control major cell cycle transitions and coordinate chromosome folding. Most well-studied eukaryotes rely on a conserved set of factors, which are divided among two loosely-defined groups, …
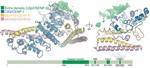
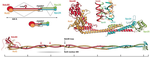
The structure of the Ctf19c/CCAN from budding yeast
Eukaryotic kinetochores connect spindlemicrotubules to chromosomal centromeres. A group of proteins called the Ctf19 complex (Ctf19c) in yeast and the constitutive centromere associated network (CCAN) in other organisms creates the foundation of a kinetochore. The Ctf19c/CCAN influences the timing …
Kinetochore function from the bottom up
During a single human lifetime, nearly one quintillion chromosomes separate from their sisters and transit to their destinations in daughter cells. Unlike DNA replication, chromosome segregation has no template, and, unlike transcription, errors frequently lead to a total loss of cell viability. …
Molecular structures of yeast kinetochore subcomplexes and their roles in chromosome segregation
Kinetochore molecular architecture exemplifies “form follows function.” The simplifications that generated the one-chromosome:one-microtubule linkage in point-centromere yeast have enabled strategies for systematic structural analysis and high-resolution visualization of many kinetochore …
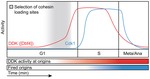
The kinetochore receptor for the cohesin loading complex
The ring-shaped cohesin complex brings together distant DNA domains to maintain, express, and segregate the genome. Establishing specific chromosomal linkages depends on cohesin recruitment to defined loci. One such locus is the budding yeast centromere, which is a paradigm for targeted cohesin …
Structural evidence for Scc4-dependent localization of cohesin loading
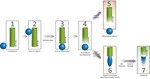
The cohesin ring holds newly replicated sister chromatids together until their separation at anaphase. Initiation of sister chromatid cohesion depends on a separate complex, Scc2(NIPBL)/Scc4(Mau2) (Scc2/4), which loads cohesin onto DNA and determines its localization across the genome. Proper …
The bioactive lipid 4-Hydroxyphenyl Retinamide inhibits flavivirus replication
Dengue virus (DENV), a member of the Flaviviridae family, is a mosquito-borne pathogen and the cause of dengue fever. The increasing prevalence of DENV worldwide heightens the need for an effective vaccine and specific antivirals. Due to the dependence of DENV upon the lipid biosynthetic machinery …
An Iml3-Chl4 heterodimer links the core centromere to factors required for accurate chromosome segregation
Accurate segregation of genetic material in eukaryotes relies on the kinetochore, a multiprotein complex that connects centromeric DNA with microtubules. In yeast and humans, two proteins – Mif2/CENP-C and Chl4/CENP-N – interact with specialized centromeric nucleosomes and establish distinct but …